I am web developer. I do .NET stuff at work. However, it is always good to try something new and different. Thus, in December 2013, I planned a rough schedule for programming self-learning in the first two months of 2014. In January, I decided to spend one hour per day to learn about Node.js and MongoDB.
I only started to learn JavaScript when I was in the first year of my university life. It turns out that it’s a very useful skill that I have because JavaScript is used very widely in my current job. However, I never tried to use JavaScript in server environment before. Here I choose Node.js because it is a very well-known server-side JavaScript example.
For MongoDB, I decided to learn it because I was invited by my friend to join a local MongoDB user group last year. It’s a group formed by developers who are very keen on learning MongoDB and other related new web technologies. After reading through their posts online, I decided to spend sometime on learning MongoDB too. Plus, the first meet up of the group that I’m always looking forward to is going to be held in this coming month, so learning MongoDB will at least help me to communicate with other members better.
Getting Started: Installing Stuff
The web development tool that I use is WebMatrix 3. The reasons that I choose WebMatrix are free, easy-to-use, and Azure-connected. In addition, WebMatrix also comes with Node.js supports and templates. Thus, with the help of WebMatrix, a simple Node.js web application can be done without too much pain.

There are three templates available for Node.js project. The Empty Site template gives a blank website setup with Node.js. This option threw me error saying “This product did not download successfully: The remote server returned an error: (404) Not Found”. According to the installer log, the error happened when downloading file ‘http://download.microsoft.com/download/6/F/4/6F439734-9589-4859-AADE-B88B0B84401E/NodeJsSite.zip‘ because the URL basically just returns error 404. Well done, Microsoft.
Hence, I’m left with two options. The Starter Site template provides a pre-built website setup with not only Node.js, but also the Express web framework. Besides Express, there are many other alternatives actually. In fact, there are reviews of different Node.js web framework available online also.
The good thing about Starter Site template is that without writing a single line of code, a beautiful web app is ready to use. Just click on the Run button in WebMatrix, the sample site will be launched in web browser. From there, you get to learn many new howtos. For example, how mobile-friendly web pages are made, how to design a web page layout with a template engine called Jade, how to enable Facebook and Twitter logins on a website, and also how to use client-side socket.io libraries to implement a chat feature in the website.

As a start, I don’t think it is a good idea to learn so many new knowledge in one month. Thus, I chose the third available template, which is the Express Site. It basically just provides a website setup with Node.js and Express without too many random stuff as what Starter Site offers.
For the modules that I use in my web app, such as Express, Jade, Mongoose, and Monk, they all can be easily installed in the NPM Gallery in WebMatrix. npm stands for Node Packaged Modules, an official package manager for Node.js and online repository for publishing packages. There is one thing that I would like to highlight is that when I didn’t run WebMatrix as administrator, the NPM Gallery seemed to have some problems. I only got to install the modules when I run WebMatrix as administrator.
Designing Web Pages
In the homepage, I would like to show a map of the place that I am currently at.
Firstly, I add the following lines in the layout.jade which is in charge of defining the general look-and-feel of each web page in my web app.
doctype html
html
head
title= title + "!"
link(rel='stylesheet', href='/stylesheets/style.css')
body
div(style="background-color: orange; color: white; height: 40px;")
div(style="padding-top: 12px; padding-left: 5px; font-weight: bold;") #{title}
block content
Secondly, I proceed to the content block for index.jade, the page displaying the map. The code below basically just loads the Google Maps API library and shows the map on the web page.
extends layout
block content
div(style="padding: 50px;")
h1= title
span Welcome to #{title}!
div(id="map-canvas")
script(type='text/javascript', src='https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/js?key=...&sensor=true')
script(type='text/javascript', src='/javascripts/initGoogleMap.js')
With such simple codes, a page with Google Maps showing the neighbourhood of user’s current location is done.
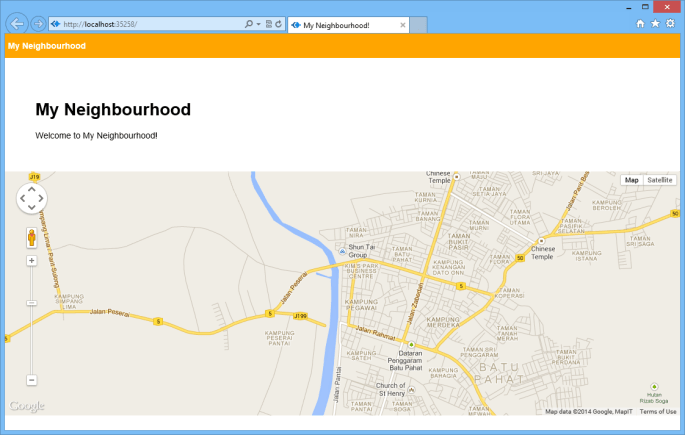
Bringing Data Into The App
A map showing user’s current location is not interesting enough. The next step will be adding an ability for the user to add marker to the map by specifying latitude and longitude.
The database system that I choose here is MongoDB. Normally people will use Mongoose, the officially supported Object Document Mapper (ODM) for Node.js. However, as a beginner, I choose to use a simpler tool, Monk. Monk offers an easier and faster way for me to learn and start working with MongoDB in Node.js.
Firstly, I need to connect to the databases and to setup routes in the server.js.
var express = require('express')
, routes = require('./routes')
, newlocation = require('./routes/newlocation')
, addlocation = require('./routes/addlocation')
, http = require('http')
, path = require('path');
...
var monk = require('monk');
var dbc = monk('localhost:27017/test');
app.get('/', routes.index(dbc));
app.get('/newlocation', newlocation.location);
app.post('/addlocation', addlocation.add(dbc));
...
After that, in the newlocation.jade, I create the form to submit the data to addlocation.js.

In the addlocation.js, there will be code to add those user-entered data to the database. With Monk, it can be done easily as shown as follows.
exports.add = function (dbc) {
return function (req, res) {
...
// Set our collection
var collection = dbc.get('LocationInfo');
// Submit to the DB
collection.insert({
"locationLatitude": locationLatitude,
"locationLongitude": locationLongitude,
"locationInfo": locationInfo
}, function (err, doc) {
if (err) {
// If it failed, return error
res.send("There was a problem adding the information to the database. Reason: " + err);
}
else {
// If it worked, set the header so the address bar doesn't still say /addlocation
res.location("");
// And forward to the homepage
res.redirect("");
}
});
}
}
Finally, I just need to retrieve the value from the database and show it in the homepage.
var collection = dbc.get('LocationInfo');
collection.find({}, {}, function (e, locations) {
res.render('index', {
"title": "My Neighbourhood",
"listOfLocations": locations
});
});

So with the help of Monk, there is even no need to define a schema at all. Even the collection LocationInfo does not need to be defined.
There is a detailed step-by-step tutorial on setting up Node.js, Express, Jade, and MongoDB available online. I personally find it to be useful because there is where I start my self-learning. In addition, here is a list of online resources that I used in the self-learning.
- How to repair my mongodb?
- Node.js – simple web server with ‘express’
- Intro to Express.js: Simple REST API app with Monk and MongoDB
Conclusion of January Self-Learning
Since I have only one hour per day to do this self-learning, so it’s quite challenging to learn all these new things in one month. In addition, there were days that I needed to work OT. So, I’m quite happy that I manage to complete this first monthly self-learning successfully. =)